Herniated Discs
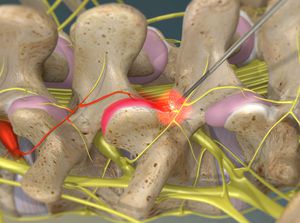
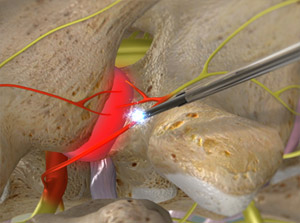
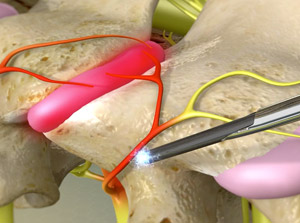
A disc herniates when its jelly-like center (nucleus) pushes against its outer ring (annulus), causing a crack in the outer layer and the soft inner material of the nucleus to rupture out of the disc. When the disc herniates out toward the spinal canal, it puts pressure on the sensitive spinal nerves, causing pain. Lifting, pulling, bending, or twisting movements often cause a herniated disc. Symptoms include numbness, tingling or weakness that radiates down the leg or arm, and back or neck pain.


 Arthritis
Arthritis